Software implementation
Contents
Software implementation#
For the full report, please see our preprint.
The information here aims to provide context to understand the documentations.
Denoising workflow#
The denoising workflow is implemented through nilearn.
Fig. 1 presents the graphic summary of the workflow.
The Python-based workflow describes the basic procedure to generate functional connectomes from fMRIPrep outputs with a Nilearn data loading routine
(e.g., NiftiMapsMasker or NiftiLabelsMasker),
fMRIPrep confounds output retrieval function (e.g., load_confounds_strategy),
and connectome generation routine (ConnectivityMeasure).
Path to the preprocessed image data is passed to load_confounds_strategy and the function fetches the associated confounds from the .tsv file.
The path of an atlas and the path of the preprocessed image file is then passed to the masker, along with the confounds, for time series extraction.
The time series are then passed to ConnectivityMeasure for generating connectomes.
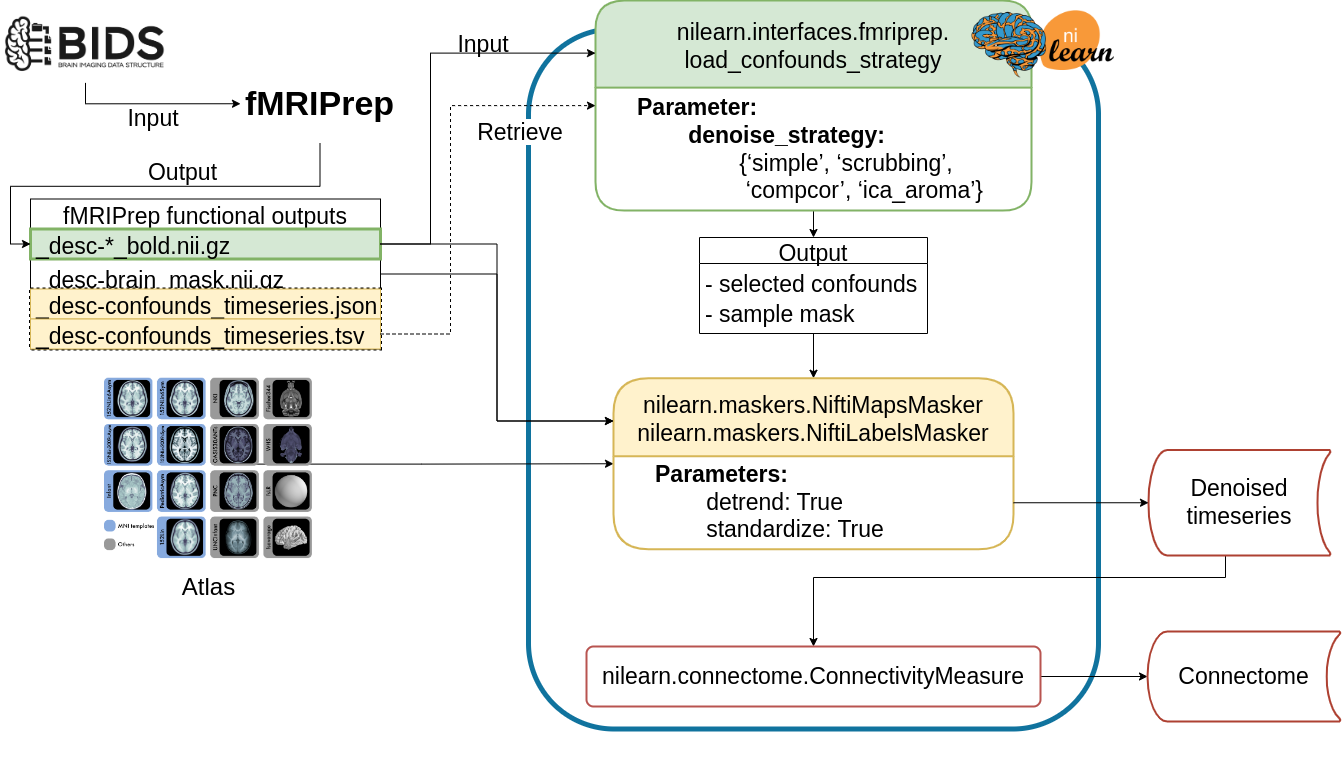
Fig. 1 Example workflow of extracting denoised timeseries and functional connectomes from fMRIPrep outputs using nilearn.#
Benchmark workflow#
Fig. 2 presents the graphic summary of the benchmark workflow.
The denoising benchmark workflow expands on the workflow in Fig. 1 (represented by the Nilearn logo in this figure). We retrieved the datasets from OpenNeuro through DataLad and all steps indicated with the arrows are implemented with bash scripts written for the SLURM scheduler. Atlases were either retrieved from the TemplateFlow archive or reformatted to fit the TemplateFlow format. The extracted time series, denoising metrics, and all metadata for generating the report are available on Zenodo.
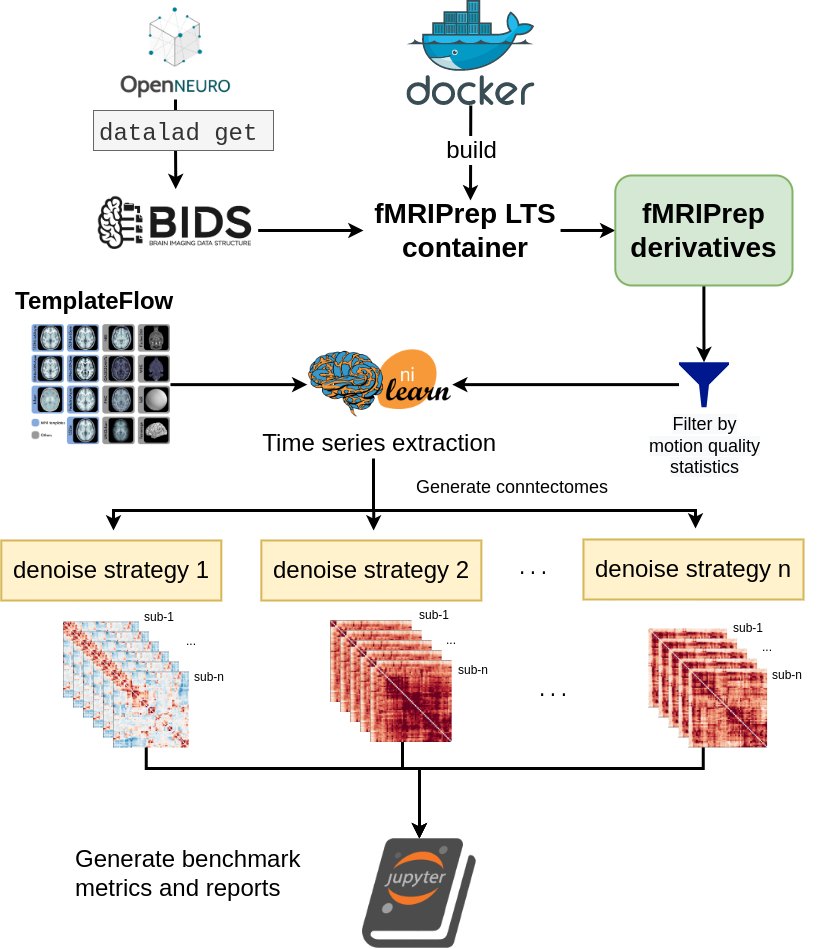
Fig. 2 Workflow of generating the full denoising benchmark.#
